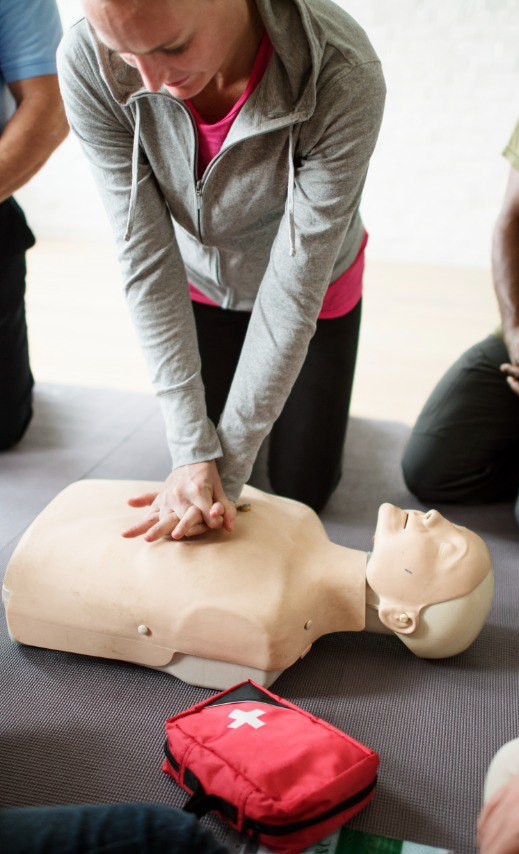
First aid is something that allows you to wait for the actual medical care and stay alive, or to help someone nearby.

So how to act in emergencies?
- The first thing to do is assess the safety of the environment. Are you safe?
- The second step is to call and wait until the ambulance or rescuers arrive. You should do it as quickly as possible.
Then everything depends on the nature of the injury. It is necessary to assess the condition of the wounded and start first aid procedures. We check the condition according to the algorithm:
- Critical bleeding. We stop it first.
- Respiratory tract. We check whether anything interferes with breathing, examine the oral cavity, and if so – remove this thing.
- Breathing. We check whether the person is breathing: whether he is conscious, whether breathing is audible, whether the chest is moving and whether it is even.
The rest – probably can wait.

Dangerous myths
If a person needs pre-medical care, it is better to try to help him or her than just leave. However, home care is full of myths. If you act on them, you can do harm.
We will discuss the most common.
- Which is better – brilliant green or iodine? None of the above. They do not disinfect the wound, but can only cause burns. What to use: chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine, if not - ethanol.
- We should lubricate the burn with oil, sour cream, or ointment. When we burn the skin, it heats up. Accordingly, we need to return the skin temperature to its original state - cool down. Most ointments, sour cream, or oil have the opposite function.
- Unconscious person – to consciousness. Loss of consciousness is a protective reaction of the body. If the body "switched off", there is a high probability that it needed it. The use of ammonia can burn the rhinopharynx.
- Foreign object in the wound – remove. This will cause such heavy bleeding that it will be extremely difficult to stop. We fix this subject and wait for doctors.
- In case of accidents – move the victim to a safe place. If possible, do not move such a person. He or she may have a spinal injury, heart attack, or stroke. In this case, the help can be very harmful.
Instructions for providing first aid
-
1. General requirements for the person who provides first aid
The first and main question we have to ask ourselves – is whether first aid is necessary?
If you see that a person needs help, and you know how to do it, but you doubt your skills, remember: you can save lives. Yes, the doctor may have to amputate the limb because of the tourniquet, but the person will be alive. Yes, you may not be able to bring a person back to life with cardiopulmonary resuscitation, but you will do your best.
Do not ignore the opportunity to help and do not underestimate yourself. You can save lives.
There is another point where we can make mistakes. It seems to us that the victim is not breathing. Conclusion - we can no longer help him. However, the conclusion is wrong. There may be reasons for the lack of breathing, and there is a chance that we will revive the person.
How to act – we will talk next.
-
Requirements for the first aid kit
Your first aid kit is something that you may need personally, as well as what first aid requires.
To conduct first aid and wait for the actual medical care, it is good to have:
- Antiseptics;
- Rubber gloves
- One-way mouth-to-mouth mask;
- Gauze, bandages;
- Adhesive plasters;
- Hemostatic tourniquets;
- Hemostatic drugs;
- Thermo blanket
You should be prepared for the fact that there will be no ideal conditions and you need to use available resources.
-
Resuscitation of the victim
We will talk about the main conditions that we can meet during hostilities.:
- Massive bleeding;
- Fracture;
- Burns;
- The person is unconscious and does not breathe;
- The victim is unconscious and breathes;
Read more details below.
-
Transportation
The main task in the transportation process – is to provide the victim with a comfortable position as soon as possible.
If there is no fracture of the spine, chest, or limbs, we can carry the victim in our arms or on a stretcher board, both in pairs or alone.
If you suspect or know about such fractures, carry the victim on a stretcher board as carefully as possible.
When transporting, think about the need to minimize any unnecessary movements, to ensure a stable position of the victim. Only then act.

MASSIVE BLEEDING
To stop any bleeding, we need to clamp the wound.
The pressure on the wound should be intense - enough to stop the bleeding.
Pressure bandage application. How and when?
To apply a tight bandage, apply a cloth roller or unwrapped bandage to increase the pressure on the wound.
- For bleeding extremities, if the bleeding is not critical.
- For bleeding of the shoulder girdle, shoulders, or forearms.
- For bleeding from the elbow, knee, and groin areas. We can combine it with bending the limbs.
- For abdominal bleeding. It is important not to insert the internal organs into the abdominal cavity. The bandage should not be too tight.
Finger pressing of the vessel to the bone. How and when?
- Forehead. It is necessary to press a temporal artery in front of an ear.
- Chin and cheek – press the external jaw artery.
- Neck and head – carotid artery on the side of the larynx.
- Shoulder and shoulder girdle – subclavian artery to the first rib in the supraclavicular fossa or axillary artery to the humerus in the axillary fossa.
- Forearm – axillary artery to the humerus in the axillary fossa.
- Thigh, shin, and foot – the femoral artery.
Applying a tourniquet. How and when?
- For bleeding extremities
If bleeding is critical, use a tourniquet or tight bandage. Apply a tourniquet to the limb above the bleeding site. If the bleeding stopped – you did everything right. Then cover the wound with a sterile bandage. Write down the time of its application.
Tamponade. How and when?
- When the wound is deep
We have to fill the cavity of the wound tightly with a cloth, and then press it with our hand or bandage it.

FRACTURE
- Closed fracture
The main task is to immobilize the limb. If possible, you can put it on a pillow or other similar surface. Put something cold on the fracture site.
If you have to transport the victim yourself, you need to apply a splint. Apply two solid objects (sticks, umbrellas, etc.) to the limb on opposite sides over the clothes and fix with a bandage or cloth. Important: the fixation should not be too tight. We fix joints above and below a fracture.
- Open fracture
Remember: if there is bleeding, stop it first. If transportation takes more than two hours, loosen the tourniquet or tight bandage for a few minutes every half hour. We need to treat the skin around the wound with antiseptic. If this is not possible, then cover the wound with a cotton cloth. After that, we put on a splint but avoid the place where the bones protrude, and take the victim to a hospital or other medical institution.
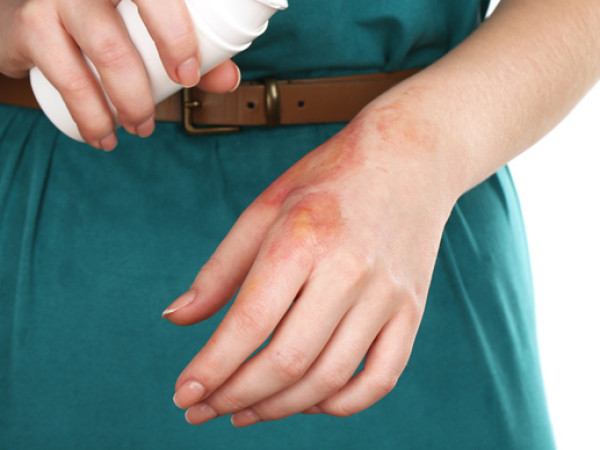
BURNS
The first step is to eliminate the source of burns. The second step is to cool the burn.
If the burn is first or second degree, the skin is red and burning or covered with blisters. We should place the affected area under a stream of cold water for about 20 minutes. Then apply a sterile bandage. Do not puncture blisters. If they are torn, apply a sterile bandage.
Third- or fourth-degree burns cause open wounds or deep tissue and muscles damage. Cover the damaged area with sterile tissue. Wrap the victim in a dry and clean blanket; ensure a calm position until medical attention arrives.
In case of facial burns, it is necessary to cover the damaged area with sterile gauze.
If eyes are affected, rinse with cold water for a long time. Another option: you can immerse the face in a container with cool water and blink often.
In case of chemical burns, we must continuously wash the affected area with water at room temperature until the arrival of doctors.
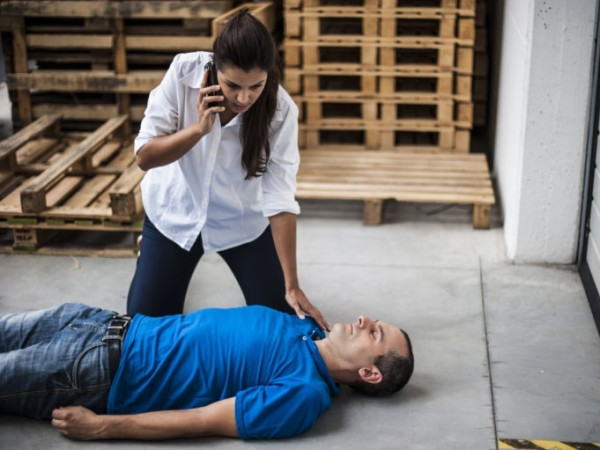

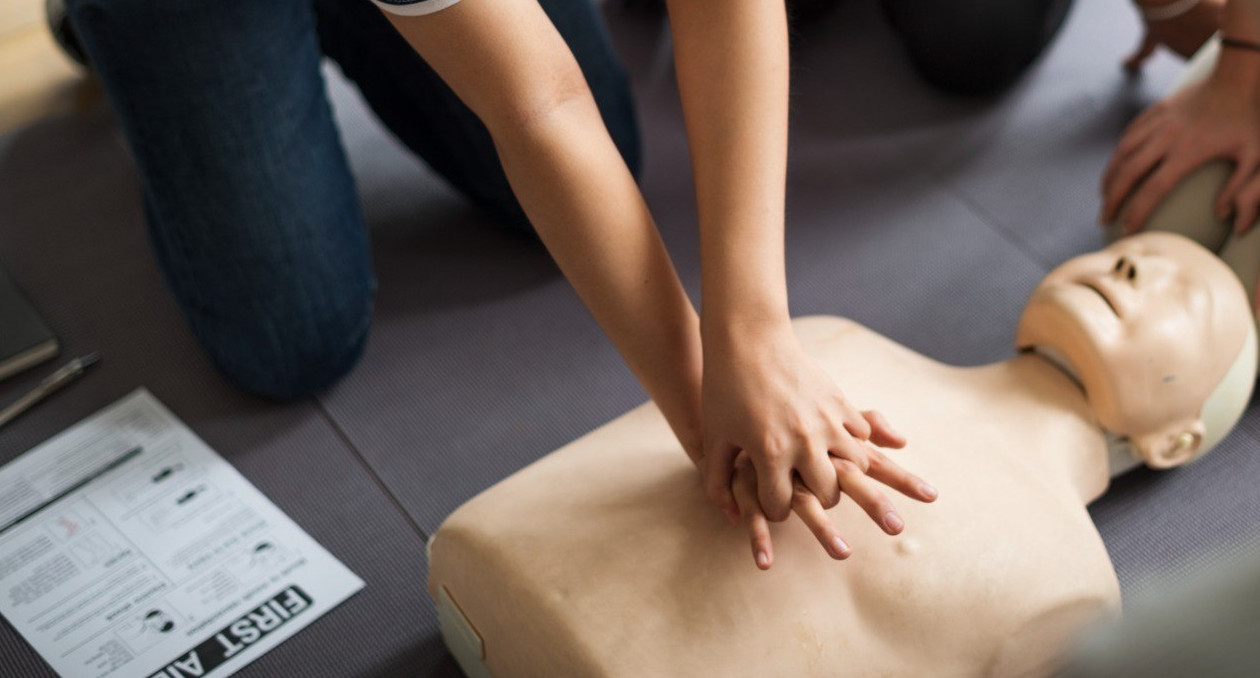
THE PERSON IS UNCONSCIOUS AND DOES NOT BREATHE
If the victim is unconscious and not breathing, quickly check the patency of the respiratory tract.
If we did not detect foreign objects, we immediately begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation or, more simply, heart massage.
So what are our actions?
- Fold the palms of your hands into the lock and press on the chest. Depth of pressure should be 5-6 cm, frequency – 100-120 pressures per minute. To determine the frequency correctly, you can sing the song "Staying alive" and press in this rhythm. It is easier that way, isn't it?
- Chest pressure can alternate with artificial respiration. If you have a valve mask, breathe into the victim's mouth 2 times using it and keep pressing. Inhales should last no more than 5 seconds.
- Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation is tiring quickly, but it can save lives. Therefore, it is better to do it together with someone else in shifts.
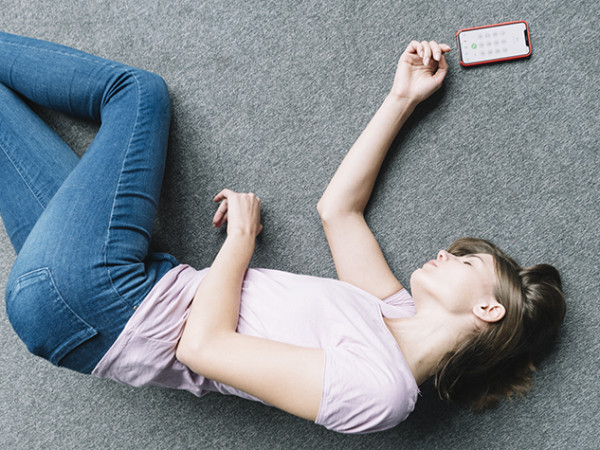

THE VICTIM IS UNCONSCIOUS, BUT BREATHS
You need to move the person to a stable lateral position. How to do it?
- Kneel next to the victim
- Raise the victim's nearest hand
- Place the victim's far hand on the opposite cheek
- Bend the victim's far leg
- Press the bent leg to your side and turn the person to the side
Done!
Do not move the victim to a stable lateral position if you suspect that he has a spinal or cervical injury
You can also learn how to provide first aid with the help of chatbots. In particular, in FastAid_bot.